3.4 Lecture 7: Meiosis-3
3.4.1 Lesson outline
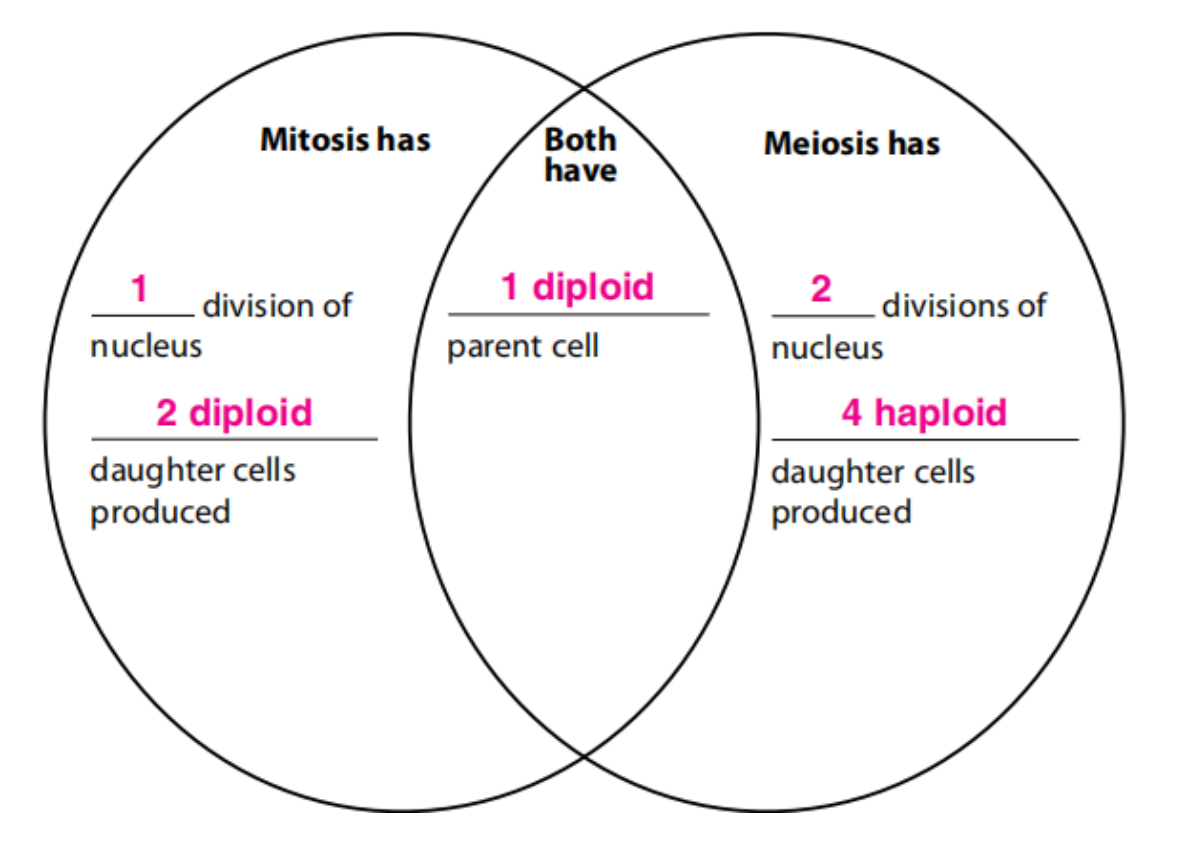
F. How do mitosis and meiosis differ?
1. During mitosis and cell division, a body cell and its nucleus divide once and produce two identical cells.
2. During meiosis, a reproductive cell and its nucleus divide twice and produce four cells––two pairs of identical haploid cells.
G. Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
1. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that have a new combination of DNA. This results in genetic variation among individuals.
2. Genetic variation gives individuals within a population slight differences that might be an advantage if the environment changes.
3. Selective breeding has been used to develop desirable traits in plants and animals.
H. Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
1. One disadvantage of sexual reproduction is that organisms have to grow and develop until they are mature enough to produce sex cells.
2. Another disadvantage is that searching for a mate takes time and energy and might expose individuals to predators, diseases, or harsh environmental conditions.
Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis and cell division
Explain why genetic variation and selective breeding are advantages of sexual reproduction.
Genetic variation: Instead of being exact genetic copies of parents, members of the same species have different traits, which enable some of them to survive environmental changes.
Selective breeding: The process of choosing and breeding individuals with desirable traits allows breeders to create offspring with those traits.
Identify two main disadvantages of sexual reproduction.
1. takes time and takes energy
2. sexual reproduction is limited by certain factors (For example, fertilization cannot take place during pregnancy, which can last as long as two years in some mammals.)
Explain how the process of meiosis relates to the way in which a child resembles but is not an exact copy of his or her parents.
Observable characteristics in a child, such as eye color, hair type and color, the shapes of facial features, and height, resemble those of his or her parents, because the child inherits portions of DNA from each parent. A child is not a exact copy of his or her parents because the child does not carry identical DNA to either parent.
3.4.2 Homework
Multiple Choice Questions
1. D
2. C
(Hint: Crossing over)
Short Answer Questions
- Organism: correct organism that produces sexually
- Mode: two different parents / egg and sperm combine in fertilization / gametes (1n) combine to form zygote (2n) / fertilization is random
- Advantage: increase genetic variations
Enrichment
1. For many generations, native plants that were resistant to disease and pests survived and reproduced. The resistant traits were passed on to their offspring. Meanwhile, those native plants that were not resistant to disease and pests died off. Eventually, the population of native plants was made up mainly of resistant plants.
2. Possible answers:
Preserve all: Many plants that have no current known value might have important uses in the future. Saving plants that aren’t useful to people is still necessary because other organisms might depend upon these plants for survival.
Preserve some: Because of budget restrictions, some plants might be targeted for preservation and others are allowed to become extinct. In this situation, it would be best to determine which plants are likely to be useful to people.